
Experiments suggest that polycarbonate fails at lower velocities with regular shaped projectiles compared to irregular ones (like fragments), meaning that testing with regular shaped projectiles gives a conservative estimate of its resistance. Levels of protection are based on the ability of the target to stop a specific type of projectile traveling at a specific speed.

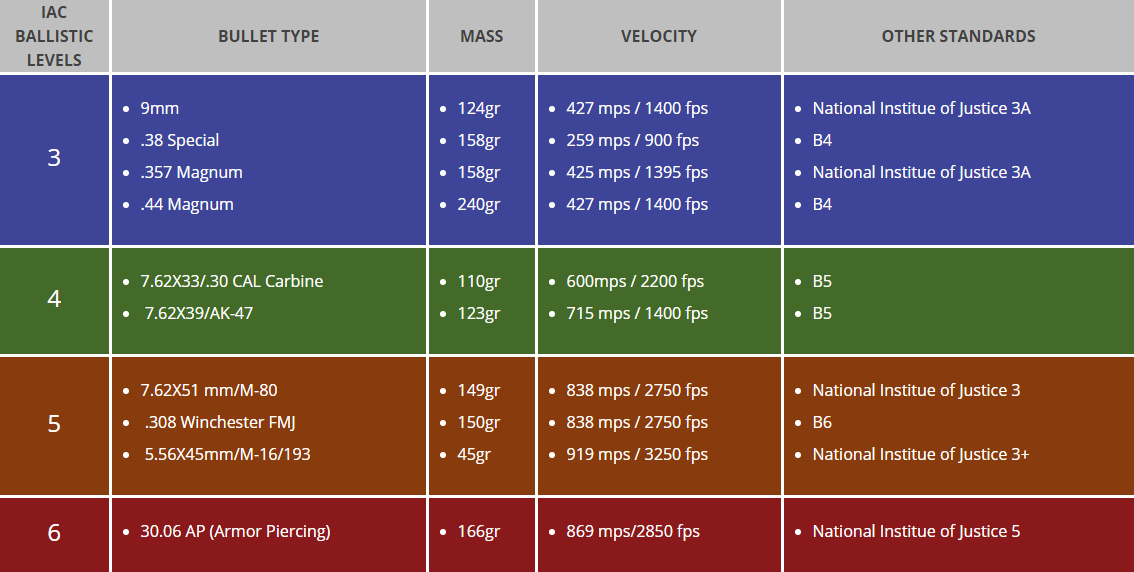
( February 2022) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message)īullet-resistant materials are tested using a gun to fire a projectile from a set distance into the material, in a specific pattern. Please improve this article by removing excessive or inappropriate external links, and converting useful links where appropriate into footnote references. This section's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines. 44 Magnum 3 shots (5 shots for NIJ IIIa)ĩmm 124gr (1400-1530fps for Level 6), 357M 158gr 44M 240gr 30-06 180gr 5.56NATO 55gr 3080-3388fps, 7.62NATO 150gr for all ratings in the above chart all copper-jacketed lead FMJ, except 30-06 is semi-wadcutter gas-checked. Sample thickness and weight for bullet-resistant glass materials It is typically thick and is usually extremely heavy. This design has been in regular use on combat vehicles since World War II. When treated with chemical processes, the glass becomes much stronger. Laminated glass layers are built from glass sheets bonded together with polyvinyl butyral, polyurethane, Sentryglas, or ethylene-vinyl acetate. The ability of the polycarbonate layer to stop projectiles with varying energy is directly proportional to its thickness, and bulletproof glass of this design may be up to 3.5 inches thick. The glass, which is much harder than plastic, flattens the bullet, and the plastic deforms, with the aim of absorbing the rest of the energy and preventing penetration. The plastic provides little in the way of bullet-resistance. The plastic in laminate designs also provides resistance to impact from physical assault from blunt and sharp objects.

Polycarbonate designs usually consist of products such as Armormax, Makroclear, Cyrolon: a soft coating that heals after being scratched (such as elastomeric carbon-based polymers) or a hard coating that prevents scratching (such as silicon-based polymers). The aim is to make a material with the appearance and clarity of standard glass but with effective protection from small arms. When a weight reduction is needed 3mm of polycarbonate (a thermoplastic) is laminated onto the safe side to stop spall. The more layers there are, the more protection the glass offers. A rough visualisation of bulletproof glass, composed of layers of plastic sheeting (grey) and layers of glass (blue)īullet-resistant glass is constructed using layers of laminated glass.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
